Fitting interface
This section summarizes how to fit copulas (and Sklar distributions) in Copulas.jl, without going into the details of each family.
Data Conventions
We work with pseudo-observations
U ∈ (0,1)^{d×n}(rows = dimension, columns = observations). You can use thepseudo()function to get such normalized ranks.The rank routines (τ/ρ/β/γ) assume pseudo-observations.
The
StatsBasefunctions for pairwise correlations use then×dconvention; when called internally, they are transposed (U) as appropriate.
Main Calls
Copula Only (Object)
using Copulas, Random, StatsBase, Distributions
Ctrue = GumbelCopula(2, 3.0)
U = rand(Ctrue, 2000)
Ĉ = fit(GumbelCopula, U; method=:mle)
ĈGumbelCopula{2, Float64}(θ = 3.101831168554804,)Returns only the fitted copula Ĉ::CT. This is a high-level shortcut.
using Plots
plot(Ĉ)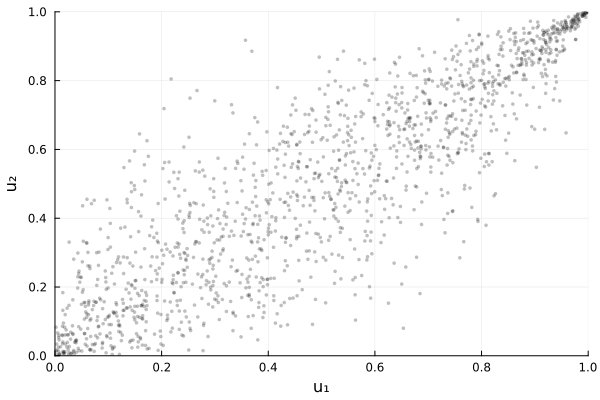
Full Model (with metadata)
M = fit(CopulaModel, GumbelCopula, U; method=:default)
M────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ CopulaModel: Archimedean d=2 ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Method: mle
Number of observations: 2000
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Fit metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Null Loglikelihood: 0.0000
Loglikelihood: 1496.9015
LR (vs indep.): 2993.80 ~ χ²(1) ⇒ p = <1e-16
AIC: -2991.803
BIC: -2986.202
Converged: true
Iterations: 4
Elapsed: 0.007s
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Dependence metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Kendall τ: 0.6776
Spearman ρ: 0.8580
Blomqvist β: 0.6813
Gini γ: 0.7293
Upper λᵤ: 0.7496
Lower λₗ: 0.0021
Entropy ι: -0.7748
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Copula parameters ] (vcov=hessian)
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Parameter Estimate Std.Err z-value p-val 95% Lo 95% Hi
θ 3.1018 0.0576 53.892 <1e-16 2.9890 3.2146Returns a CopulaModel with:
result(the fitted copula),n,ll(log-likelihood),method,converged,iterations,elapsed_sec,vcov(if available),method_details(a named tuple with method metadata).
Behavior & conventions (important)
fit operates on types, not on pre-constructed parameterized instances. Always pass a Copula or SklarDist type to
fit, e.g.fit(GumbelCopula, U)orfit(CopulaModel, SklarDist{ClaytonCopula,Tuple{Normal,LogNormal}}, X). If you already have a constructed instanceC0, re-estimate its parameters by callingfit(typeof(C0), U).Default method selection: each family exposes the list of available fitting strategies via
_available_fitting_methods(CT, d). Whenmethod = :defaultthe first element of that tuple is used. Example:Copulas._available_fitting_methods(MyCopula, d).CopulaModelis the full result object returned by the fits performed viaDistributions.fit(::Type{CopulaModel}, ...). The light-weight shortcutfit(MyCopula, U)returns only a copula instance; usefit(CopulaModel, ...)to get diagnostics and metadata.
CopulaModel Interface (summary)
The CopulaModel{CT} <: StatsBase.StatisticalModel type stores the result and supports the standard StatsBase interface:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
nobs(M) | Number of observations |
loglikelihood(M) | Log-likelihood at the optimum |
deviance(M) | Deviance (= −2 loglikelihood) |
coef(M) | Estimated parameters |
coefnames(M) | Parameter names |
vcov(M) | Var–cov matrix |
stderror(M) | Standard errors |
confint(M) | Confidence intervals |
aic(M) | Akaike Information Criterion |
bic(M) | Bayesian Information Criterion |
aicc(M) | Corrected AIC (small-sample) |
hqc(M) | Hannan–Quinn criterion |
By default, the returned CopulaModel contains a lot of extra statistics, that you can see by printing the model in the REPL.
vcov and inference notes
- The
CopulaModelfieldvcov(exposed asStatsBase.vcov(M)) contains the estimated covariance matrix of the fitted copula parameters when available. Many families supply:vcovvia themetaNamedTuple returned by_fit(for examplemeta.vcov). Ifvcov === nothingthe package cannot computestderrororconfintand those helpers will throw.
TODO: add an example here.
Consider adding a small bootstrap wrapper for robust CIs when the Hessian is unreliable.
Joint margin fitting + copula (Sklar)
:ifm: fits parametric margins and projects to pseudo-data with their CDFs.:ecdf: uses pseudo-empirical observations (ranks).
Notes:
sklar_method=:ifmfits parametric margins first and converts observations to pseudo-scale via the fitted marginal CDFs.sklar_method=:ecdfuses empirical pseudo-observations (ranks). Choose:ifmwhen margins are believed parametric and you want a model-based projection; choose:ecdfto avoid margin misspecification.margins_kwargsis currently a singleNamedTupleapplied to every marginal fit. If you need different options per margin, fit margins manually (callDistributions.fitfor each marginal type) and then call the copula fit on the pseudo-data yourself.The model's
null_llfield (used in LR tests) is computed as the sum of the marginal logpdfs under the fitted margins; LR tests compare the fitted copula vs independence while keeping the same margins.
S = SklarDist(ClaytonCopula(2, 5), (Normal(), LogNormal(0, 0.5)))
X = rand(S, 1000)
Ŝ = fit(CopulaModel, SklarDist{ClaytonCopula,Tuple{Normal,LogNormal}}, X;
sklar_method=:ifm, # or :ecdf
copula_method=:default, # see next section.
margins_kwargs=NamedTuple(), copula_kwargs=NamedTuple()) # options will be passed down to fitting functions.
Ŝ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ CopulaModel: SklarDist ] (Copula=Archimedean d=2, Margins=(Normal, LogNormal))
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Copula: Archimedean d=2
Margins: (Normal, LogNormal)
Methods: copula=mle, sklar=ifm
Number of observations: 1000
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Fit metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Null Loglikelihood: -2108.1906
Loglikelihood: -1130.2458
LR (vs indep.): 1955.89 ~ χ²(1) ⇒ p = <1e-16
AIC: 2262.492
BIC: 2267.399
Converged: true
Iterations: 3
Elapsed: 0.006s
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Dependence metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Kendall τ: 0.7203
Spearman ρ: 0.8891
Blomqvist β: 0.7530
Gini γ: 0.7972
Upper λᵤ: 0.0000
Lower λₗ: 0.8741
Entropy ι: -0.9615
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Copula parameters ] (vcov=hessian)
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Parameter Estimate Std.Err z-value p-val 95% Lo 95% Hi
θ 5.1505 0.1682 30.625 <1e-16 4.8208 5.4801
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Marginals ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Margin Dist Param Estimate Std.Err 95% CI
#1 Normal μ -0.0693 0.0307 [-0.1295, -0.0091]
σ 0.9709 0.0217 [0.9283, 1.0134]
#2 LogNormal μ -0.0153 0.0160 [-0.0465, 0.0160]
σ 0.5044 0.0113 [0.4823, 0.5265]plot(Ŝ.result)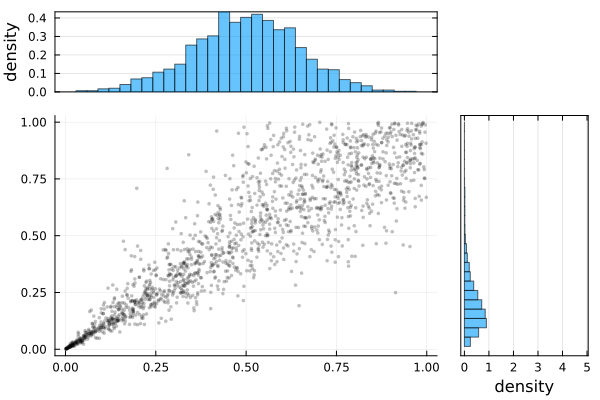
Available fitting methods
The names and availiability of fitting methods depends on the model. You can check what is available with the following internal call :
Copulas._available_fitting_methods(ClaytonCopula, 3)(:mle, :itau, :irho, :ibeta)The first method in the list is the one used by default.
Short description
:mle— Maximum likelihood overU. Recommended when there is a stable density and good reparameterization.:itau— Kendall's inverse: matches the theoreticalτ(C)with the empiricalτ(U). Ideal for single-parameter families or when a reliable monotone inverse exists.:irho— Spearman's inverse: analogous toρ; can operate with scalar or matrix objectives (e.g., multivariate Gaussians).:ibeta— Blomqvist's inverse: scalar; only works if the family has ≤ 1 free parameter.
Note: Rank-based methods require that the number of free parameters not exceed the information of the coefficient(s) used; in the case of
:ibeta, this is explicitly enforced.
In extreme value copulas, the :mle/:iupper variants can rely on the Pickands function (A(t)) and its derivatives (A, dA, d²A) with Brent-type numerical inversion.
Implementing fitting for a new family (contributor checklist)
When you add a new copula family, implement the following so the generic fit flow works seamlessly:
_example(CT, d)— return a representative instance (used to obtain default params and initial values)._unbound_params(CT, d, params)— transform the familyNamedTupleparameters to an unconstrainedVector{Float64}used by optimizers._rebound_params(CT, d, α)— invert_unbound_params, returning aNamedTuplesuitable forCT(d, ...)construction._available_fitting_methods(::Type{<:YourCopula}, d::Int)— declare supported methods (examples::mle, :itau, :irho, :ibeta, ...)._fit(::Type{<:YourCopula}, U, ::Val{:mle})(and otherVal{}methods) — implement the method and return(fitted_copula, meta::NamedTuple); include keys such as:θ̂,:optimizer,:converged,:iterationsand optionally:vcov.
Place this checklist and a minimal _fit skeleton in docs/src/manual/developer_fitting.md where contributors can copy/paste and adapt. ````