Fitting interface
This section summarizes how to fit copulas (and Sklar distributions) in Copulas.jl, without going into family-specific details.
Data conventions
We work with pseudo-observations
U ∈ (0,1)^{d×n}(rows = dimensions, columns = observations). Usepseudos(X)to obtain normalized ranks from raw dataX.Rank-based routines (tau / rho / beta / gamma) assume pseudo-observations.
StatsBasepairwise correlation helpers use then×dconvention; internally we transpose as needed (e.g.,U').
Main calls
Copula only (object)
using Copulas, Random, StatsBase, Distributions, Plots
Ctrue = GumbelCopula(2, 3.0)
U = rand(Ctrue, 2_000)
Ĉ = fit(GumbelCopula, U; method=:mle)
ĈGumbelCopula{2, Float64}(θ = 3.101831168554782,)Returns only the fitted copula Ĉ::CT (high-level shortcut).
Full model (with metadata)
M = fit(CopulaModel, GumbelCopula, U; method=:default)
M────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ CopulaModel: Archimedean d=2 ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Method: mle
Number of observations: 2000
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Fit metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Null Loglikelihood: 0.0000
Loglikelihood: 1496.9015
LR (vs indep.): 2993.80 ~ χ²(1) ⇒ p = <1e-16
AIC: -2991.803
BIC: -2986.202
Converged: true
Iterations: 4
Elapsed: 0.007s
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Dependence metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Kendall τ: 0.6776
Spearman ρ: 0.8580
Blomqvist β: 0.6813
Gini γ: 0.7351
Upper λᵤ: 0.7496
Lower λₗ: 0.0021
Entropy ι: -0.7644
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Copula parameters ] (vcov=hessian)
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Parameter Estimate Std.Err z-value p-val 95% Lo 95% Hi
θ 3.1018 0.0576 53.892 <1e-16 2.9890 3.2146Returns a CopulaModel with:
result(the fitted copula),n,ll(log-likelihood),method,converged,iterations,elapsed_sec,vcov(if available),method_details(aNamedTuplewith method-specific metadata).
Behavior & conventions (important)
operates on types, not on pre-constructed instances. Pass a copula or Sklar type, e.g. fit(GumbelCopula, U)orfit(CopulaModel, SklarDist{ClaytonCopula,Tuple{Normal,LogNormal}}, X). If you already have an instanceC0, re-estimate its parameters withfit(typeof(C0), U).Default method selection. Each family exposes allowed fitting strategies via
_available_fitting_methods(CT, d). Withmethod = :default, the first element of that tuple is used. Example:Copulas._available_fitting_methods(MyCopula, d).CopulaModelis the full result returned byDistributions.fit(::Type{CopulaModel}, ...). The lightweight shortcutfit(MyCopula, U)returns only a copula; usefit(CopulaModel, ...)to get diagnostics and metadata.
CopulaModel interface (summary)
The CopulaModel{CT} <: StatsBase.StatisticalModel supports the standard StatsBase API and a few additional fields:
| Function / Field | Description |
|---|---|
Field M.ll | Log-likelihood at the optimum (numeric field stored in the model). |
nobs(M) | Number of observations used in the fit. |
deviance(M) | Deviance (= −2 · M.ll). |
nullloglikelihood(M) | Log-likelihood under independence with same margins (available for Sklar fits). |
nulldeviance(M) | Deviance of the null model (−2 · nullloglikelihood(M)). |
aic(M) / bic(M) | Information criteria from |
aicc(M) / hqc(M) | Information criteria from |
coef(M) / coefnames(M) | Estimated parameters and their names. |
vcov(M) | Parameter variance–covariance matrix (may be nothing). |
stderror(M) / confint(M; level=0.95) | Standard errors and Wald confidence intervals (require vcov(M) ≠ nothing). |
residuals(M; transform=:uniform | :normal) | Rosenblatt residuals on [0,1] or Normal scale (requires method_details[:U]). |
predict(M; what=:cdf|:pdf|:simulate, ...) | CDF/PDF at newdata, or simulation (nsim; default nsim = M.n if nsim == 0). |
Examples
# Information criteria
StatsBase.aic(M)
StatsBase.bic(M)
Copulas.aicc(M)
Copulas.hqc(M)-2989.7465401775894# Standard errors and Wald CIs
StatsBase.stderror(M)
StatsBase.confint(M; level=0.95)([2.989022251918489], [3.214640085191075])# Rosenblatt residuals
R = StatsBase.residuals(M; transform=:uniform)
RN = StatsBase.residuals(M; transform=:normal)
(size(R), size(RN))((2, 2000), (2, 2000))# Predictions and simulation
P = StatsBase.predict(M; what=:cdf, newdata=rand(2, 5)) # CDF at 5 points
F = StatsBase.predict(M; what=:pdf, newdata=rand(2, 5)) # PDF at 5 points
X̂ = StatsBase.predict(M; what=:simulate, nsim=1_000) # simulate 1,000 obs
(size(P), size(F), size(X̂))((5,), (5,), (2, 1000))Covariance estimation (vcov) and inference
When fitting with fit(CopulaModel, ...), the keyword vcov=true triggers estimation of the parameter covariance matrix.
Default.
vcov = true. Covariance is computed automatically unless the user disables it (vcov=false) or a family turns it off internally (e.g.,TCopula,FGMCopula,tEVCopula) when required derivatives are not implemented.
The internal dispatcher _vcov(CT, U, θ̂; method, override) selects the estimator:
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
:hessian | Inverse observed information (−Hessian of the log-likelihood). Default for method = :mle. |
:godambe | Godambe (sandwich) estimator based on score-type functions. Used for rank-based fits. |
:godambe_pairwise | Pairwise Godambe using all variable pairs. |
:jackknife | Leave-one-out jackknife approximation (robust fallback). |
:bootstrap | Bootstrap approximation (√n resamples, up to 200). |
You can override the choice via vcov_method:
M2 = fit(CopulaModel, GumbelCopula, U; method=:mle, vcov=true, vcov_method=:bootstrap, derived_measures=false)
StatsBase.vcov(M2) isa AbstractMatrixtrueEach method returns a symmetric (positive semi-definite) matrix Vθ, stored as M.vcov and exposed by StatsBase.vcov(M).
Fallbacks. If non-finite values appear in Hessian/Godambe computations, the algorithm automatically falls back (first to :bootstrap; if instability persists, to :jackknife).
Note. In the example above we set derived_measures=false, which disables the automatic calculation and storage of dependence measures (e.g., Kendall’s τ, Spearman’s ρ, Blomqvist’s β, , Gini's γ, upper/lower tail coefficients, entropy). By default this is enabled. Disabling it reduces computation and memory footprint and omits the Dependence metrics section in the REPL summary.
Joint margins + copula (Sklar)
You can pass the sklar_method parameter as:
:ifm: fits parametric margins and maps data to pseudo-scale via their CDFs.:ecdf: uses empirical pseudo-observations (ranks).
Notes
Use
sklar_method = :ifmwhen margins are plausibly parametric and you want a model-based projection; use:ecdfto avoid margin misspecification.margins_kwargsis a singleNamedTupleapplied to every marginal fit. For heterogeneous options, fit margins manually and then fit the copula on the resulting pseudo-data.The model’s
null_ll(for LR tests) is the log-likelihood under independence with the same margins.
S = SklarDist(ClaytonCopula(2, 5), (Normal(), LogNormal(0, 0.5)))
X = rand(S, 1000)
Ŝ = fit(CopulaModel, SklarDist{ClaytonCopula,Tuple{Normal,LogNormal}}, X;
sklar_method=:ifm, # or :ecdf
copula_method=:default, # see next section.
margins_kwargs=NamedTuple(), copula_kwargs=NamedTuple()) # options will be passed down to fitting functions.
Ŝ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ CopulaModel: SklarDist ] (Copula=Archimedean d=2, Margins=(Normal, LogNormal))
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Copula: Archimedean d=2
Margins: (Normal, LogNormal)
Methods: copula=mle, sklar=ifm
Number of observations: 1000
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Fit metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Null Loglikelihood: -2166.1883
Loglikelihood: -1188.6310
LR (vs indep.): 1955.11 ~ χ²(1) ⇒ p = <1e-16
AIC: 2379.262
BIC: 2384.170
Converged: true
Iterations: 3
Elapsed: 0.005s
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Dependence metrics ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Kendall τ: 0.7189
Spearman ρ: 0.8880
Blomqvist β: 0.7515
Gini γ: 0.7727
Upper λᵤ: 0.0000
Lower λₗ: 0.8732
Entropy ι: -0.9889
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Copula parameters ] (vcov=hessian)
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Parameter Estimate Std.Err z-value p-val 95% Lo 95% Hi
θ 5.1139 0.1688 30.301 <1e-16 4.7831 5.4447
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[ Marginals ]
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Margin Dist Param Estimate Std.Err 95% CI
#1 Normal μ 0.0275 0.0318 [-0.0348, 0.0899]
σ 1.0063 0.0225 [0.9622, 1.0504]
#2 LogNormal μ 0.0063 0.0160 [-0.0250, 0.0376]
σ 0.5047 0.0113 [0.4826, 0.5268]plot(Ŝ.result)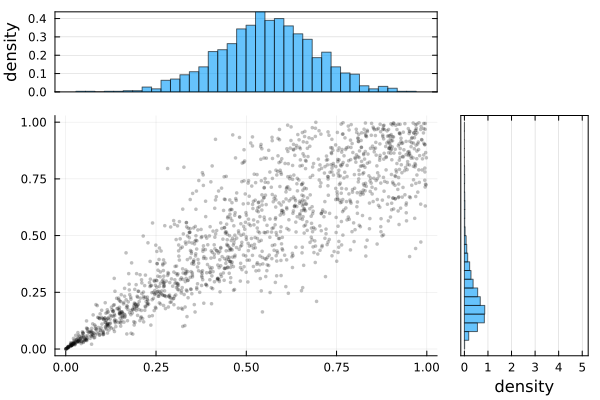
Available fitting methods
The names and availability of fitting methods depend on the family. Inspect them via:
Copulas._available_fitting_methods(ClaytonCopula, 3)(:mle, :itau, :irho, :ibeta)The first method in the list is used by default.
Short descriptions
:mle— Maximum likelihood overU. Recommended when a stable density and a good reparameterization exist.:itau— Kendall inverse: matches theoreticaltau(C)to empiricaltau(U). Ideal for single-parameter families with a monotone inverse.:irho— Spearman inverse: analogous torho; can use scalar or matrix objectives (e.g., multivariate Gaussians).:ibeta— Blomqvist inverse: scalar; only valid for families with ≤ 1 free parameter.
Remark. Rank-based methods require that the number of free parameters does not exceed the information contained in the chosen coefficient(s);
:ibetaenforces this explicitly.
For extreme-value copulas, :mle / :iupper may rely on the Pickands function A(t) and its derivatives (A, dA, d²A) with Brent-type inversion.
Nonparametric fits (Empirical Copulas)
In addition to parametric families (MLE / rank-based), Copulas.jl exposes several nonparametric or empirical constructions that can be fit through the same high-level API:
EmpiricalCopula(Deheuvels)BetaCopulaBernsteinCopulaCheckerboardCopulaEmpiricalEVCopula(built fromEmpiricalEVTail, bivariate extreme-value case)
See the dedicated page for theory, properties, and references: Empirical models.
All StatsBase / StatsModels functionality works identically for these copulas: you can call coef, aic, bic, deviance, predict, residuals, etc., and obtain a full CopulaModel object with the same structure and printing behavior.
The only difference is that empirical models are parameter-free (dof(M) = 0), so vcov(M), stderror(M), and confint(M) return nothing, and information criteria reduce to AIC = BIC = −2 · loglikelihood. Otherwise, all features—including the computation of dependence measures and the REPL summary—behave exactly the same.